BUY CBD PRODUCTS

Buy CBD products including CBD oils, CBD salves in South Africa, free shipping for orders over R899. Joint pain, Joint swelling, Muscle pain, Inflammatory skin conditions, Psoriasis, Eczema, Itchy Rashes, Bacterial infections (MRSA), Neck and back pain, Contact dermatitis, Acne, Nerve pain.
WHAT EXACTLY IS CBD
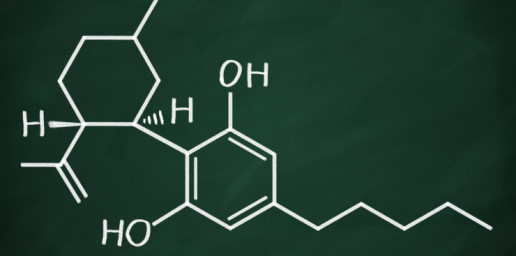
CBD, otherwise known as cannabidiol, is a natural chemical compound that comes from the hemp plant. It is one of over 85 compounds found in hemp, known as cannabinoids. However, CBD is not a psychotropic cannabinoid like THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol, found in marijuana; CBD does not produce intoxication or euphoria.
In plain terms, CBD will not get you high; it works for natural pain-relief, anti-inflammatory and therapeutic purposes. Cannabinoids have their effect mainly by interacting with receptors in your brain and body. THC reacts with a specific receptor of which CBD has very little to no impact. New studies are providing mounting evidence that CBD reacts to other receptors in the brain and body contributing to therapeutic effects.
Because of the way that CBD reacts to the body, this is the safer, less controversial alternative with all the health benefits still intact. CBD has multiple uses. The oil can be taken orally, rubbed on the skin and sometimes inhaled via vapor to produce its effects.
Cannabidiol (CBD) came out to the world in a big way after this simple plant chemical stopped an epileptic seizure in its tracks on U.S. national television. In the time since, many enthusiasts have realized that this miracle compound can stop spasms, calm anxiety and soothe those in chronic pain.
Although CBD still has an effect on your body, consuming CBD by itself isn’t going to send you on the cerebral adventure associated with THC. For decades, medical professionals and the general public overlooked CBD because psychotropic cannabis took center stage.
MEDICAL POTENTIAL OF CBD

Now, the medical potential of CBD has taken cannabis to mainstream audiences. Preclinical trials over the past four decades have found that the cannabinoid shows promise as an:
- Anti-inflammatory
- Antioxidant
- Neuroprotectant
- Anxiolytic
- Antidepressant
- Analgesic
- Antitumoral agent
- Antipsychotic
CBD is often used by patients in the form of an oil. Patients with chronic conditions, such as cancer and epilepsy, often use medical cannabis oil extracted from high-CBD/THC varieties of cannabis.